
Elements to calculate the play at the cut
The cylinder walls are cooled either by outside air or by water.
The rings loose a part of their accumulated energy on contact with the cylinder and their temperature is the average of the cylinder wall and that of the piston head. The rings grow whilst getting hotter. Their temperature is higher than the cylinders. The rings absorb the energy from the pistons. The cylinder walls are cooled by the outside air or by the water circulation.
The expansion of the cylinders and their bore is difficult to estimate in most cases as the engine block the cylinders sit in have a complex shape and it is difficult to confirm that the bores increase as much as the basic calculations would indicate.
In any case the coefficient of expansion of the cast iron rings are higher than the cast iron cylinders. The length of the ring must be short enough that at operation temperature the ends do not meet. This means that the length of the ring is shorter than the circumference of the cylinder, especially for the more critical case of when the temperature difference between the ring and the cylinder is at its most. (Starting, bad lubrication, high revs…).
The coefficient of expansion of a standard cast iron ring is:
- from 20 à 200°C : 1,07 millimetre per meter for every 100°C variation
- from 200 à 500°C : 1,30 mm per meter for every 100°C variation
For applications other than internal combustion engines, the play will be determined by the application and the operating temperatures, the nature of the liquid or the gas involved, etc…
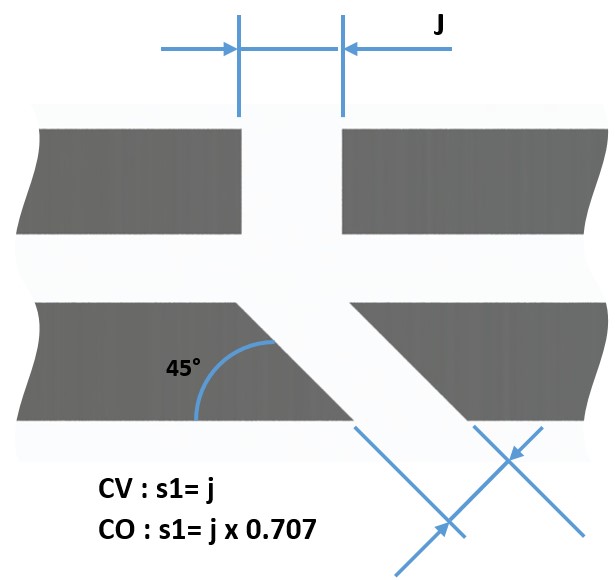
For the segments with an oblique cut at 45°, the play (S1) is equal to the gap j x 0.707.
For hydraulic applications, choosing an oblique cut reduces the risk of scratching the cylinders.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Recommended hydraulics |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
nominal diameter |
Oblique |
Upright |
|||
|
de |
à |
mini |
maxi |
mini |
maxi |
|
25,00 |
49,00 |
0,05 |
0,15 |
0,10 |
0,25 |
|
50,00 |
75,00 |
0,10 |
0,20 |
0,15 |
0,30 |
|
76,00 |
110,00 |
0,15 |
0,30 |
0,20 |
0,35 |
|
110,00 |
140,00 |
0,20 |
0,35 |
0,30 |
0,50 |
|
141,00 |
200,00 |
0,30 |
0,45 |
0,40 |
0,60 |